Diabetes is not an illness that can be cured. Once you have been diagnosed with diabetes, you will need lifelong monitoring and treatment. It is vitally important that you learn to keep your blood glucose between 4 and 10 mmol/L.
Type 1 or type 2
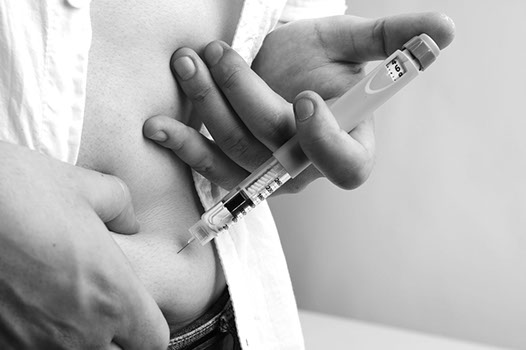
- For type 1 diabetes administering insulin is necessary and vitally important. If you have type 1 diabetes, you must always have insulin within reach. It is also recommended that you inform family members, friends etc about (where to find) your insulin. It is also advisable that several people in your surroundings learn how to administer your insulin injection.
- For type 2 diabetes, medication to lower blood glucose levels and a lifestyle change are often enough.
- A combination of tablets and insulin and a change in lifestyle (exercise and a healthier diet) may also apply.
Doctors and practitioners
You will have dealings with various specialists during your illness. These include:
- GP or his assistant
- Internist
- Diabetes nurse
- Dieticiant
Your healthcare professional is always your first point of contact. If you have any questions, notice changes in the pattern of your illness, develop certain complaints, your healthcare professional is your point of contact. Many people search for information themselves, for example, by talking with fellow sufferers or checking the internet. Both are valuable resources, but keep in mind that diabetes and your treatment plan are very personal.